Nvidia’s strategic move to establish manufacturing facilities in the United States, in partnership with companies like TSMC, Foxconn, and others, offers a multitude of benefits, driven by a combination of economic, geopolitical, and technological factors.
1. Supply Chain Resilience and Security
Mitigation of Geopolitical Risk: By producing its advanced AI chips and supercomputers on U.S. soil, Nvidia reduces its reliance on overseas manufacturing hubs, particularly in Asia. This move directly addresses rising geopolitical tensions and export controls, which have the potential to disrupt the global semiconductor supply chain.
Strengthened Supply Chain: The company’s U.S.-based manufacturing strategy, which includes fabrication, packaging, assembly, and testing, creates a more localized and robust supply chain. This diversification makes it less vulnerable to international trade disputes, tariffs, and other external disruptions.
National Security Alignment: The decision aligns with U.S. government priorities to increase domestic semiconductor output and ensure technological self-reliance, which is seen as a matter of national security.
2. Economic and Job Growth
Job Creation: The initiative is expected to create a significant number of direct and indirect jobs across various sectors, including engineering, operations, and logistics, as new facilities are built and operated.
Economic Impact: The investment, which could amount to hundreds of billions of dollars, stimulates economic growth in the regions where facilities are located, such as Arizona and Texas. This includes building out a new AI manufacturing ecosystem.
Government Incentives: The move is supported by U.S. government programs like the CHIPS and Science Act, which provides grants and tax credits to incentivize domestic semiconductor production.
3. Technological Advancement and Innovation
Proximity to Demand: Manufacturing AI infrastructure in the U.S. places production closer to the major data centers and companies that are the primary customers for these technologies, creating a more direct and efficient manufacturing pipeline.
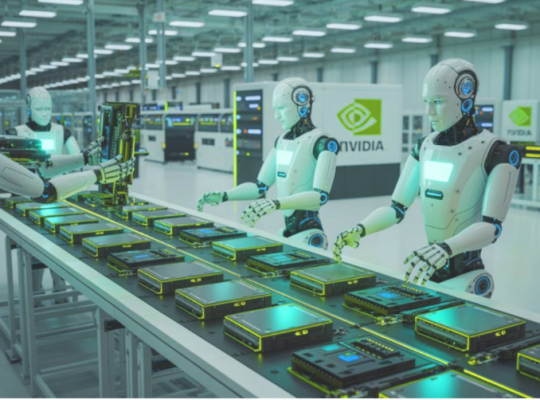
Leveraging Internal Technology: Nvidia is using its own advanced technologies, such as NVIDIA Omniverse, to create “digital twins” of the factories. These virtual models allow for predictive modeling and layout optimization before physical construction begins. The company also plans to use AI-driven robotics (NVIDIA Isaac GR00T) to automate precision tasks, showcasing its own innovations in industrial settings.
Market Leadership: By manufacturing its most advanced AI chips and supercomputers domestically, Nvidia strengthens its position as a leader in the rapidly growing AI industry, positioning itself to meet the soaring demand for AI infrastructure.
For Nvidia
Supply Chain Resilience: This is a major driver for the change. By moving a portion of its manufacturing to the U.S., Nvidia reduces its reliance on a concentrated, overseas supply chain, particularly in Asia. This mitigates risks from geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, and international trade disputes (like tariffs and export controls), ensuring a more stable and reliable supply of its crucial AI chips and supercomputers.
Meeting Demand: The demand for AI chips is skyrocketing. Domestic manufacturing allows Nvidia to better meet this growing demand by establishing production closer to its major customers, particularly data centers and “AI factories” in the United States.
Technological Alignment: Nvidia is leveraging this shift to showcase its own technologies. It plans to use its Omniverse platform to create “digital twins” of the new factories for optimization and its Isaac GR00T robotics for automation. This not only makes the factories more efficient but also serves as a real-world demonstration of its AI and robotics products.
Government Incentives: The move aligns with U.S. government initiatives, such as the CHIPS and Science Act, which provides significant funding, grants, and tax credits to incentivize domestic semiconductor production. This can help offset the higher costs associated with U.S. manufacturing.
For the U.S. Economy
Job Creation: Nvidia’s investments, in partnership with other companies like TSMC, Foxconn, and Amkor, are expected to create a substantial number of jobs. This includes direct jobs in manufacturing, packaging, and testing facilities, as well as indirect jobs in supporting industries.
Economic Growth and Investment: The commitment of hundreds of billions of dollars in new infrastructure, including manufacturing plants in states like Arizona and Texas, stimulates significant economic activity and investment in the country. This helps to establish and bolster regional technology ecosystems.
Technological Leadership: By becoming a hub for the production of cutting-edge AI chips and supercomputers, the U.S. solidifies its position as a global leader in artificial intelligence and semiconductor technology. This move is seen as a way to enhance technological self-reliance and national security in a critical industry.
Blueprint for the Future: If successful, Nvidia’s model of highly automated, U.S.-based AI manufacturing could serve as a blueprint for other companies and countries, demonstrating a path toward building robust and resilient sovereign AI infrastructure.